Agronomy

Soils, like people, can be healthy or unhealthy. We’ve recently learned how important the microbes inside our bodies are to human health. Likewise, soil health depends on a complex group of microbes. These bacteria and fungi recycle nutrients and prepare the soils to better support plants.

Potatoes are the most consumed vegetable in the United States. According to the USDA, US farmers grew more than 42 billion lbs. of potatoes in 2019. That’s 128 lbs. of potatoes per person.

You may have heard the term “carbon sequestration.” In its basic terms, it refers to keeping and returning carbon to the soil. Since carbon is an element, how and why should this be done?
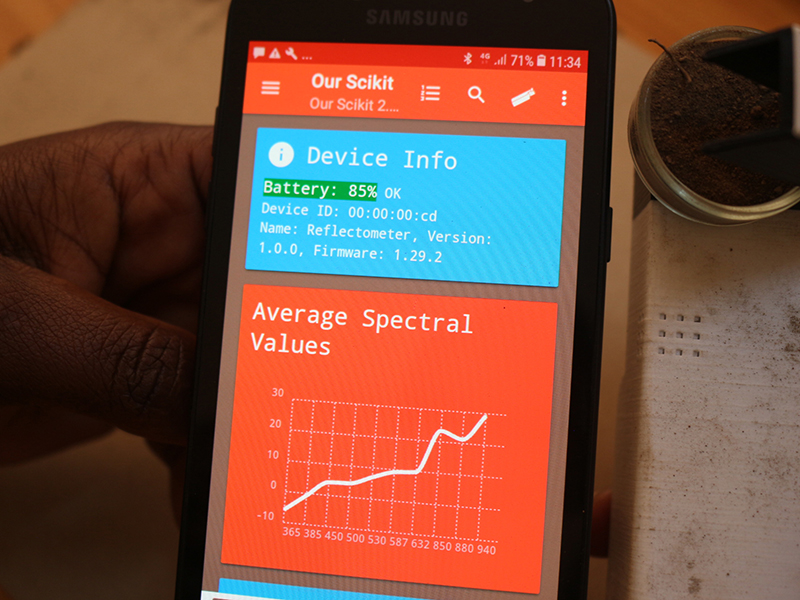
The amount of carbon in farm soils is important to farmers. Soils with high carbon contents tend to provide better yields. They also tend to have more resilience to weather-related crop failure. But measuring the amount of carbon in soil can be expensive and involve several steps. That can make it hard to collect this critical information in regions like sub-Saharan Africa.
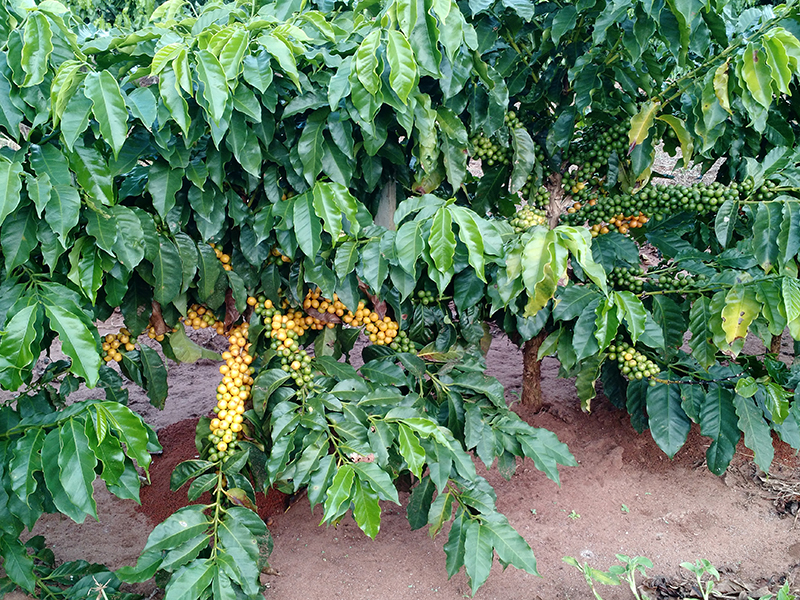

The perfect cup of morning coffee. Before you even purchase the beans at the store, many things must go right before that great-tasting coffee can be poured into your favorite mug. It starts in the soil where farmers grow the beans. For example, Brazil is the world’s biggest coffee producer, and the soils there can cause problems for coffee plants.
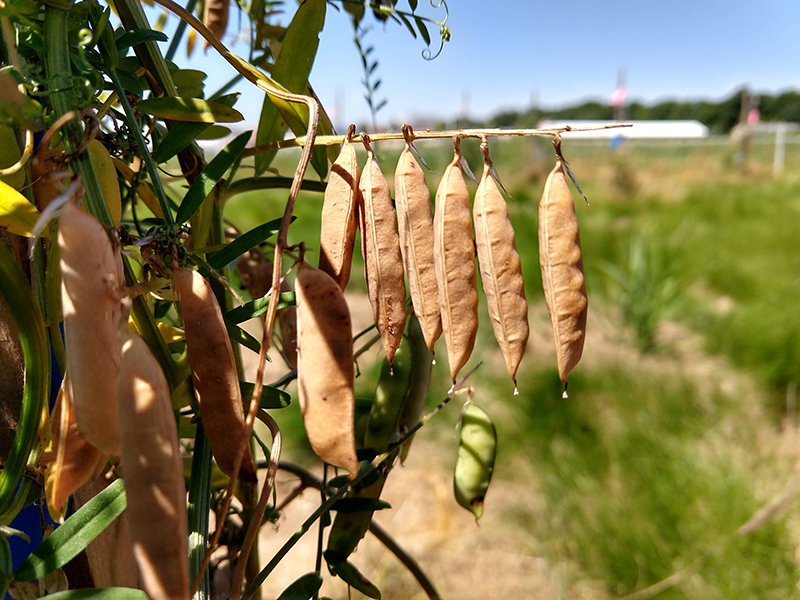

Both chemical fertilizers and cover crops can help build the nitrogen content in soil. But cover crops come with many other benefits, like improving soil structure and boosting beneficial microbes.





