Soil Science
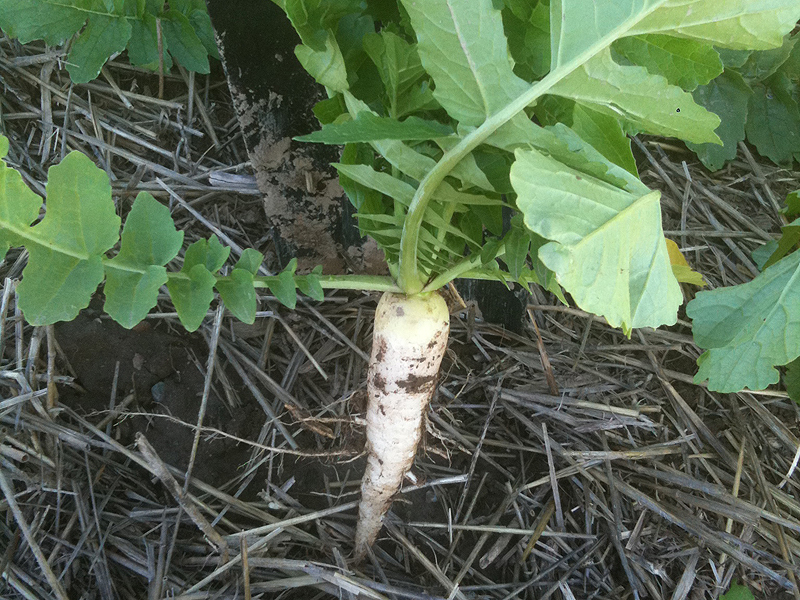

When you think of a radish, you may think of the small, round, crunchy, red-and-white vegetable that is sliced into salads. You might be surprised to learn that a larger, longer form of this root vegetable is being used in agriculture as a cover crop.

As the growing season progresses, you might not notice much about what’s happening to plants under the soil. Most of us pay attention to new shoots, stems, leaves, and eventually the flowers and crop we intend to grow. We might think of roots as necessary, but uninteresting, parts of the crop production process.


Soil gets tired. After years of supporting a rotating cast of crops, the soil’s nutrient supply is often exhausted. The tilling, turning, and planting also degrade the organic matter in the soil and its ability to stay hydrated.


We often “flush it and forget it” when it comes to waste from toilets and sinks. However, it’s important to be able to track this wastewater to ensure it doesn’t end up in unwanted places. A group of Canadian scientists has found an unlikely solution.
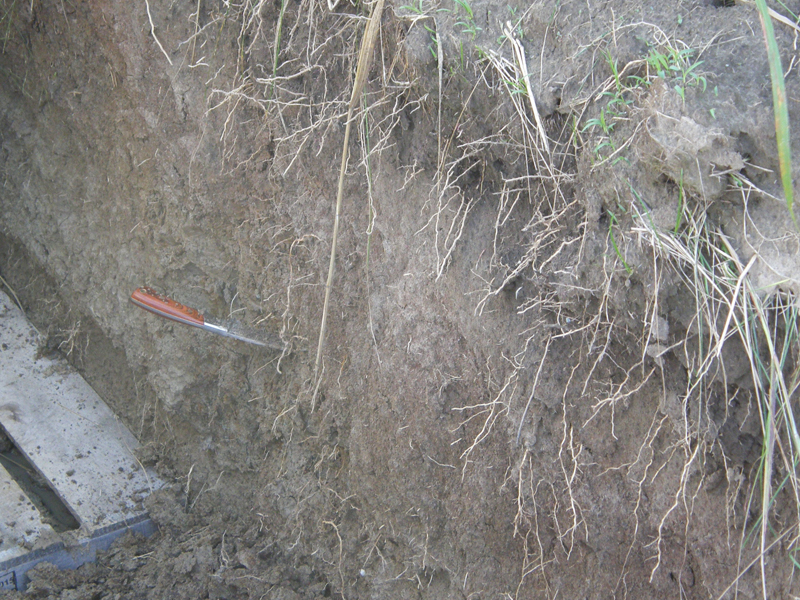

Soil characteristics like organic matter content and moisture play a vital role in helping plants flourish. It turns out that soil temperature is just as important. Every plant needs a certain soil temperature to thrive. If the temperature changes too quickly, plants won’t do well. Their seeds won’t germinate or their roots will die.“Most plants are sensitive to extreme changes in soil temperature,” said Samuel Haruna, a researcher at Middle Tennessee State University. “You don’t want it to change too quickly because the plants can’t cope with it.”
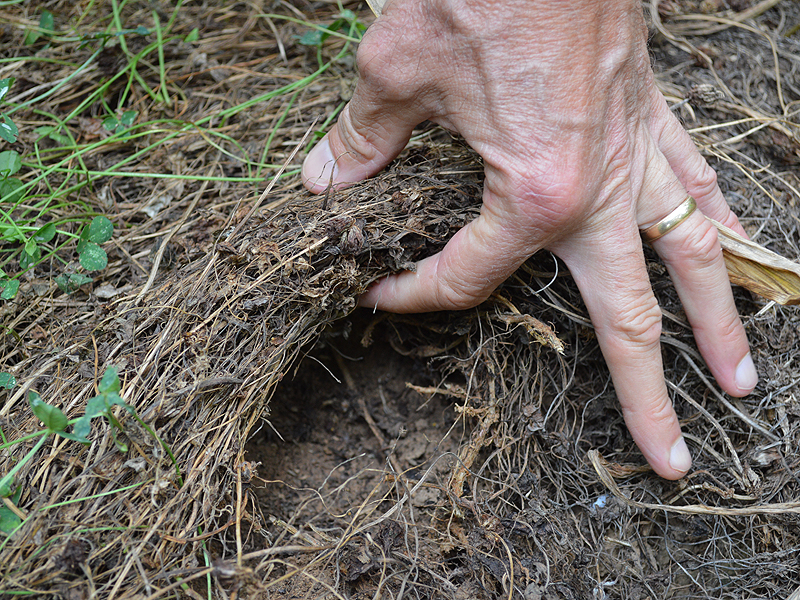

Living mulch functions like mulch on any farm or garden except — it’s alive. No, it’s not out of the latest horror movie; living mulch is a system farmers can use to benefit both profits and the soil. While the system has been around for a while, scientists at the University of Georgia are making it more efficient and sustainable.
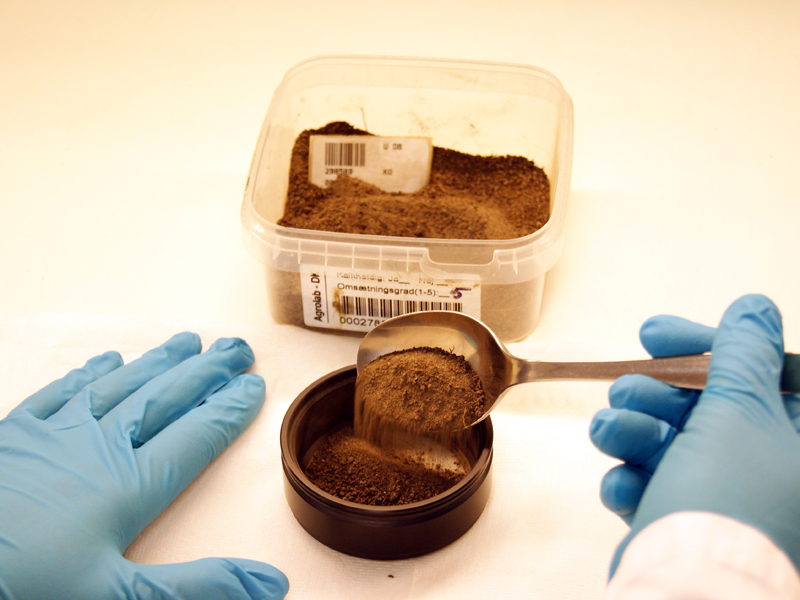

Farmers and gardeners know their soil texture can make a big difference in their success. Different plants have different needs for water, nutrients, and air. When they grow in soil that has the right texture, it is easier to deliver the right amount of water, fertilizer, or pesticide to the plants. Then they grow better.
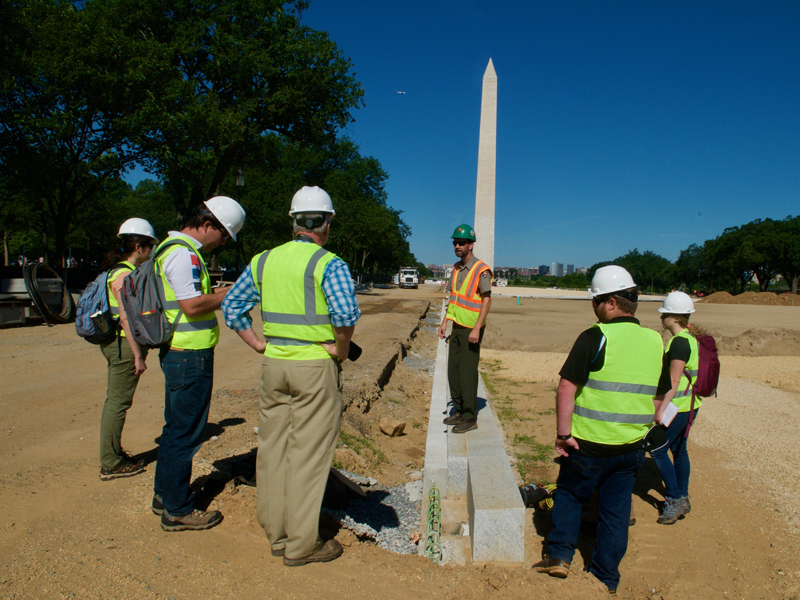

It’s not every day United States history mixes with microbes in the soil. But when the turf on the National Mall in Washington, D.C. was replaced, it offered scientists the opportunity to study changes in the soil underneath.

Producers sometimes face challenges that go deep into the soil. They need answers to help the soil, on site. A portable field sensor can accurately measure minerals in soils more easily and efficiently than existing methods. And a research team, including a middle school student and her scientist father, can confirm it.
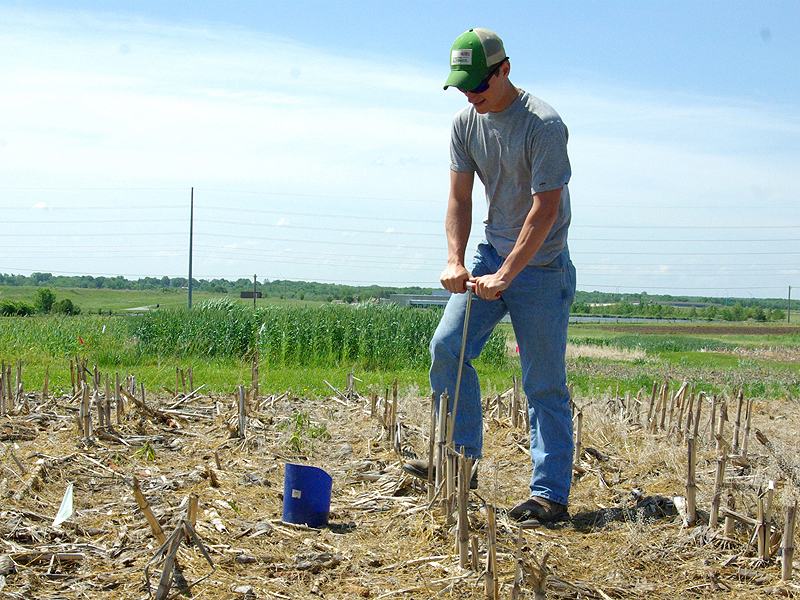

All soils are not equal. Rich loams support the world’s most productive agricultural regions, including swaths of the American Midwest. But in some parts of the Midwest, including areas in Missouri and Illinois, claypan soils dominate. And where claypans reign, problems for producers abound. New research from the University of Missouri could help claypan farmers improve yields while saving costs.
